Anatomy
Anatomy of the Human Body
Differences between Male and Female Skull
August 7/2025
General knowledge
I think that most people have a general understanding of the differences between men and women.
These usually includes larger and sturdier bones in men, and softer, smaller bones in women.
However, I'd like to adress these things a bit more specificaly and put them into perspective to show where the differences occur the most and what to watch out for.It's also important to remember that it's a spectrum on which male and female bones don't follow strict rules. For example, even if pronounced eyebrow bossing is typically seen as a male trait, it doesn’t mean women can’t have larger eyebrow bones while still maintaining softer features elsewhere.
You have to take these indications and information as a tool in your artworks. Learning how to create more feminine or masculine features will help you tell the character’s story, capture the character’s vibe, or simply move a portrait toward the part of the spectrum you wish to give.
The big shape
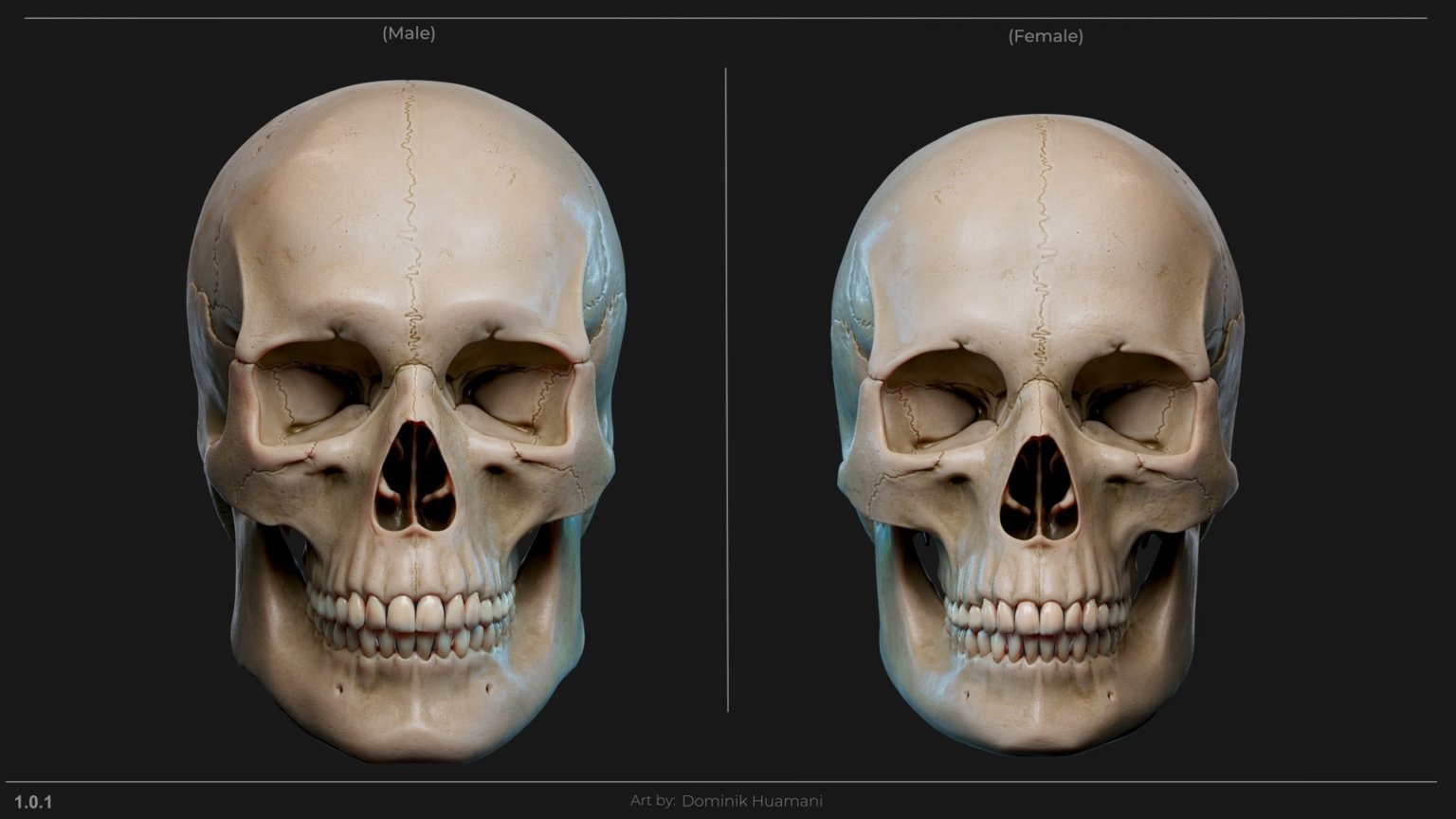
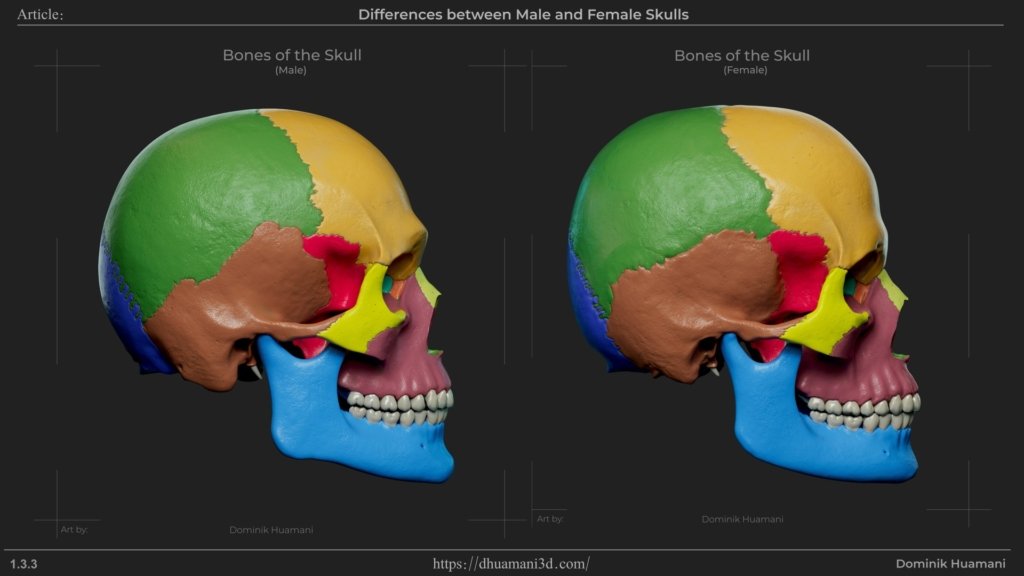
As in many animals, nature has done it so that male’s are often physically larger and stronger. Therefore the body adapts to reinforce these traits, and one of the main differences in skulls is their size and angular features. As mentioned before, female bones in general tend to be lighter, smoother and smaller.
At first glance you should be able to tell the difference even without any prior knowledge. I made these skulls based on face scans to capture the main shapes, but I also adjusted certain details to better represent each gender, helping you to more easily recognize both prominent and subtle features.
As you can see in the image bellow (1.0.1)
These skulls are exaggerated in certain areas to make the features easy to read. Even so ,I bet that you could think of someone for example a woman with a wide jaw or prominent brow ridges, or a man with a smoother neuro-cranium(the braincase) and softer eye area and that’s fine.
I mentioned a spectrum in which these bones grow and I want you to keep that in mind as along your artistic journey you will encounter many people going outside these “rules” but it’s for us artist to take inspiration and knowledge to bend these natural rules knowingly with intent and not randomly.
So let’s keep in mind the differences in bone between genders.Overall Male will have Sturdier and Larger bones meaning teeth and skull will grow visibly bigger, whereas women tend to have smaller and smoother shapes while still maintaining all the same features, just not as pronounced.
Glabella and Supericilliary Arches
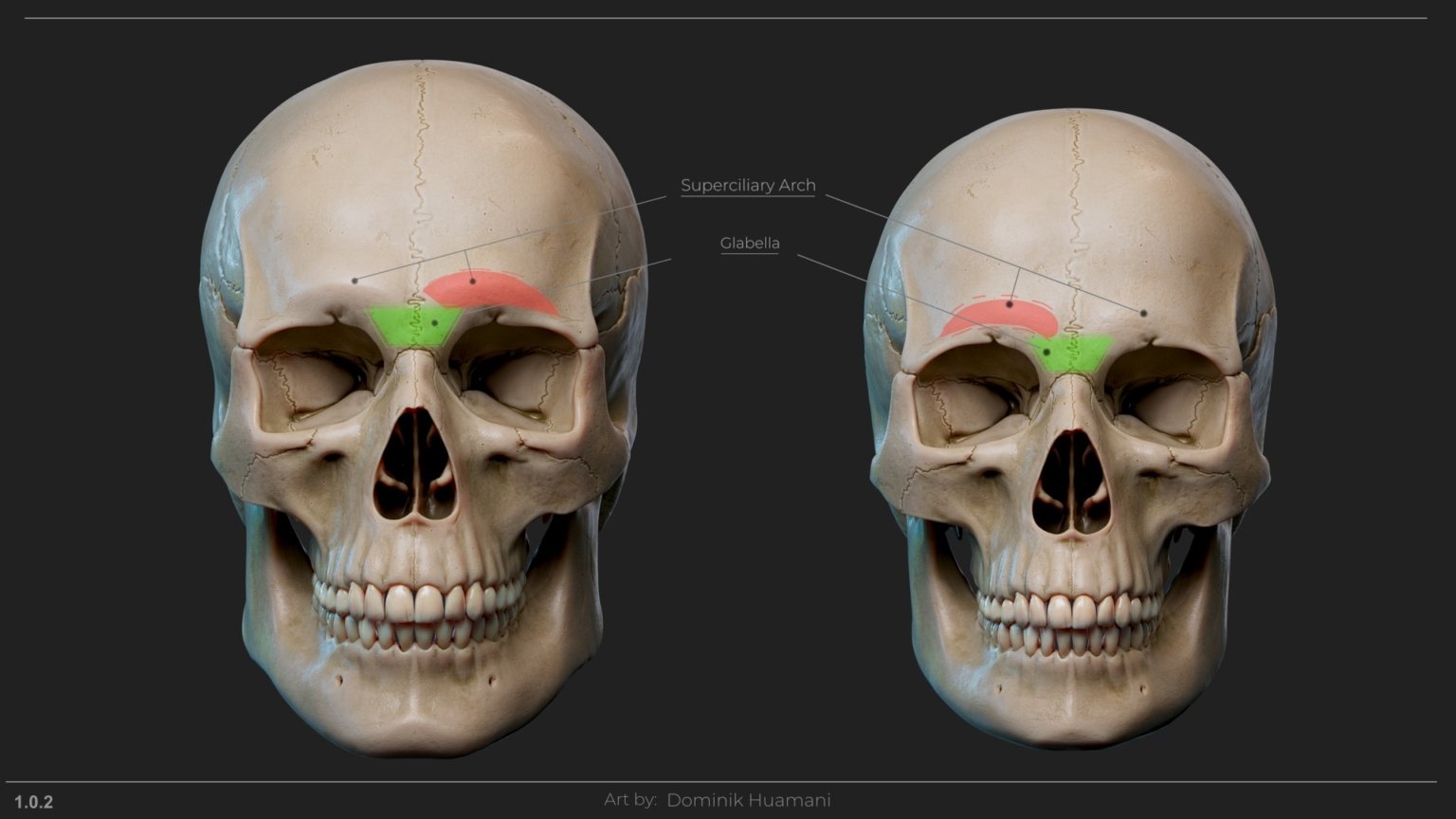
Let’s first define what is glabella and what are Superciliary Arches(SA[1.0.2]).
Glabella
Glabella is an anatomical landmark. It lies between superciliary arches where bones connect(GreenColor).
It has a trapezoid shape and creates a plane change from profile.
Sutures are the ridges on the that make the separation of different parts and the one where Glabella lies is called Metopic.
Superciliary Arch
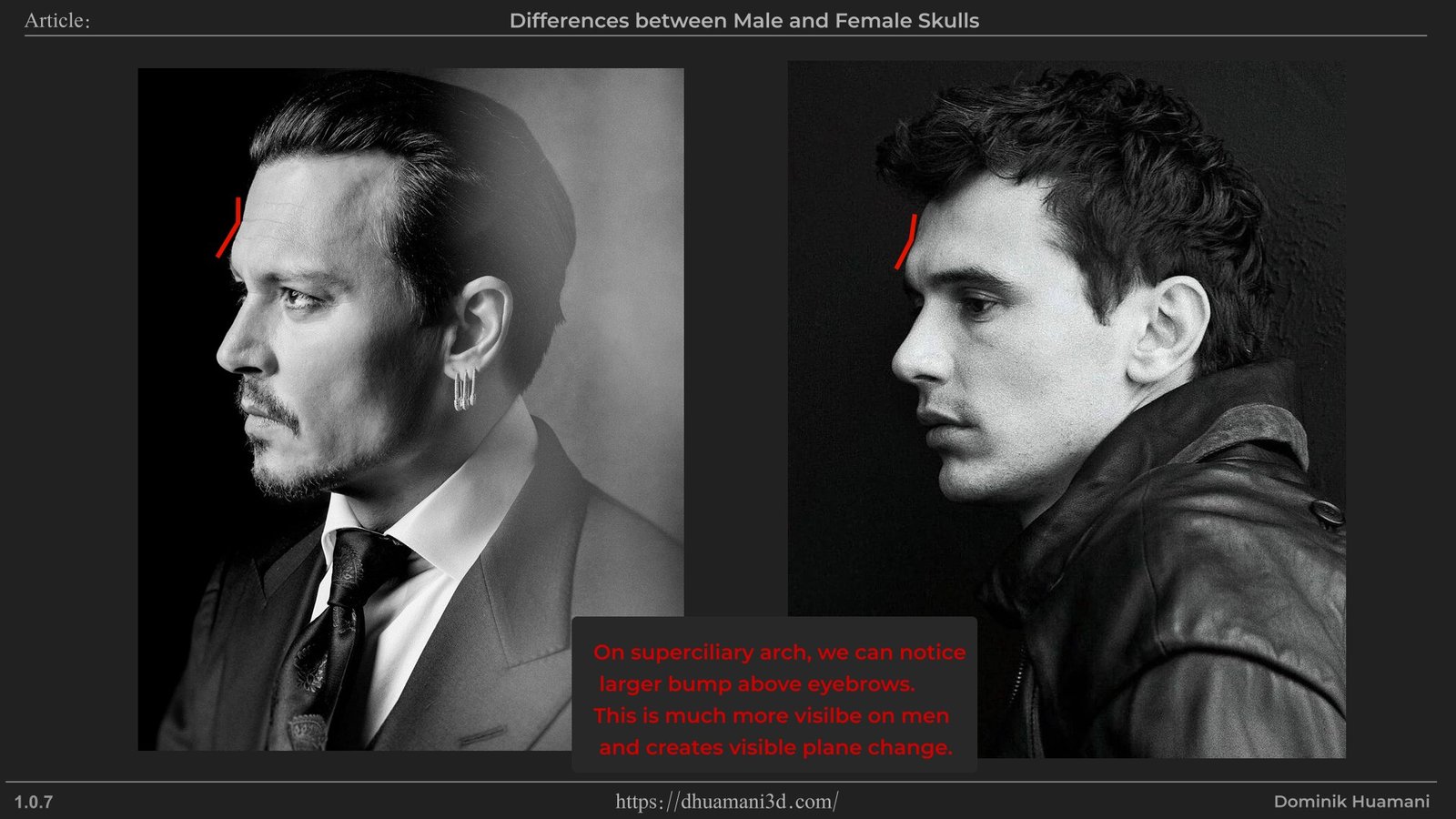
Also called Supraorbital Ridges, Supra meaning Above and Orbital meaning Eye orbits.
It’s a raised bump above eyes on a place where Eyebrows are at. It’s a bony prominence on the frontal bone(Forehead) and it’s meant for the protection of the eyes.
There are also muscles connected to it, such as corrugator supercii which is eyebrow muscle but that’s not so important right now.
Differences
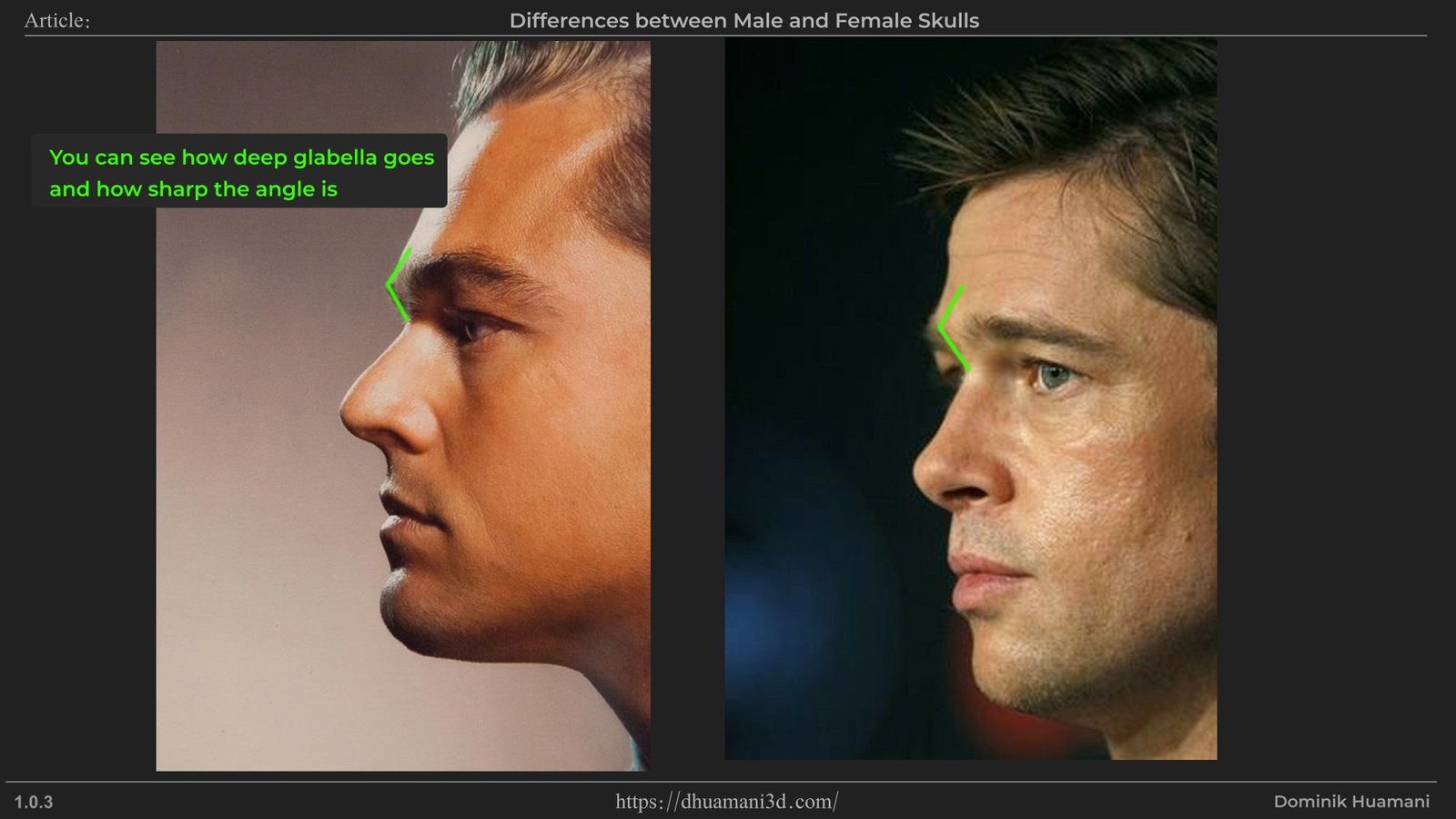
Now the differences are pretty much as most things will be and that is it's size and pronouncement.
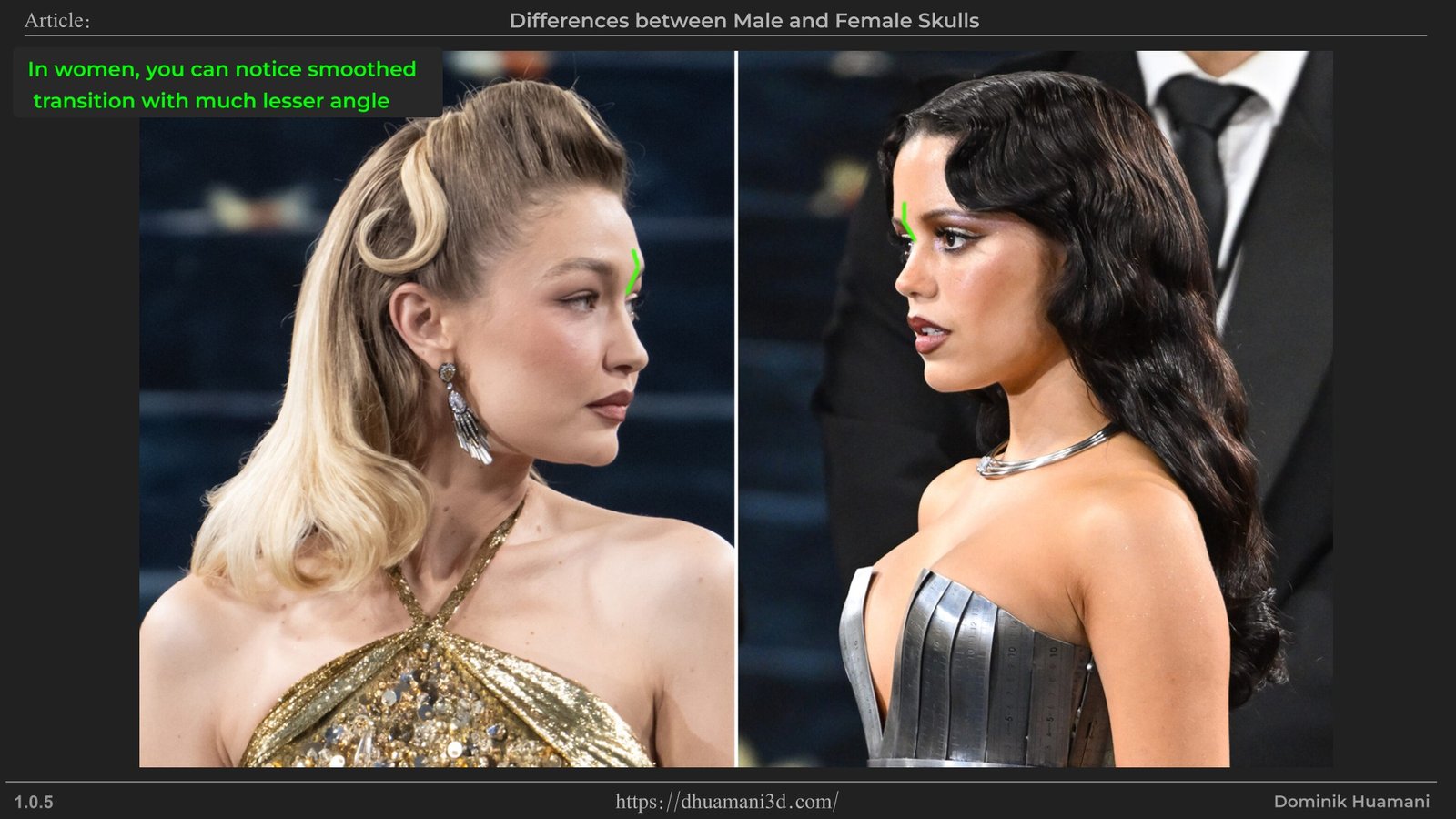
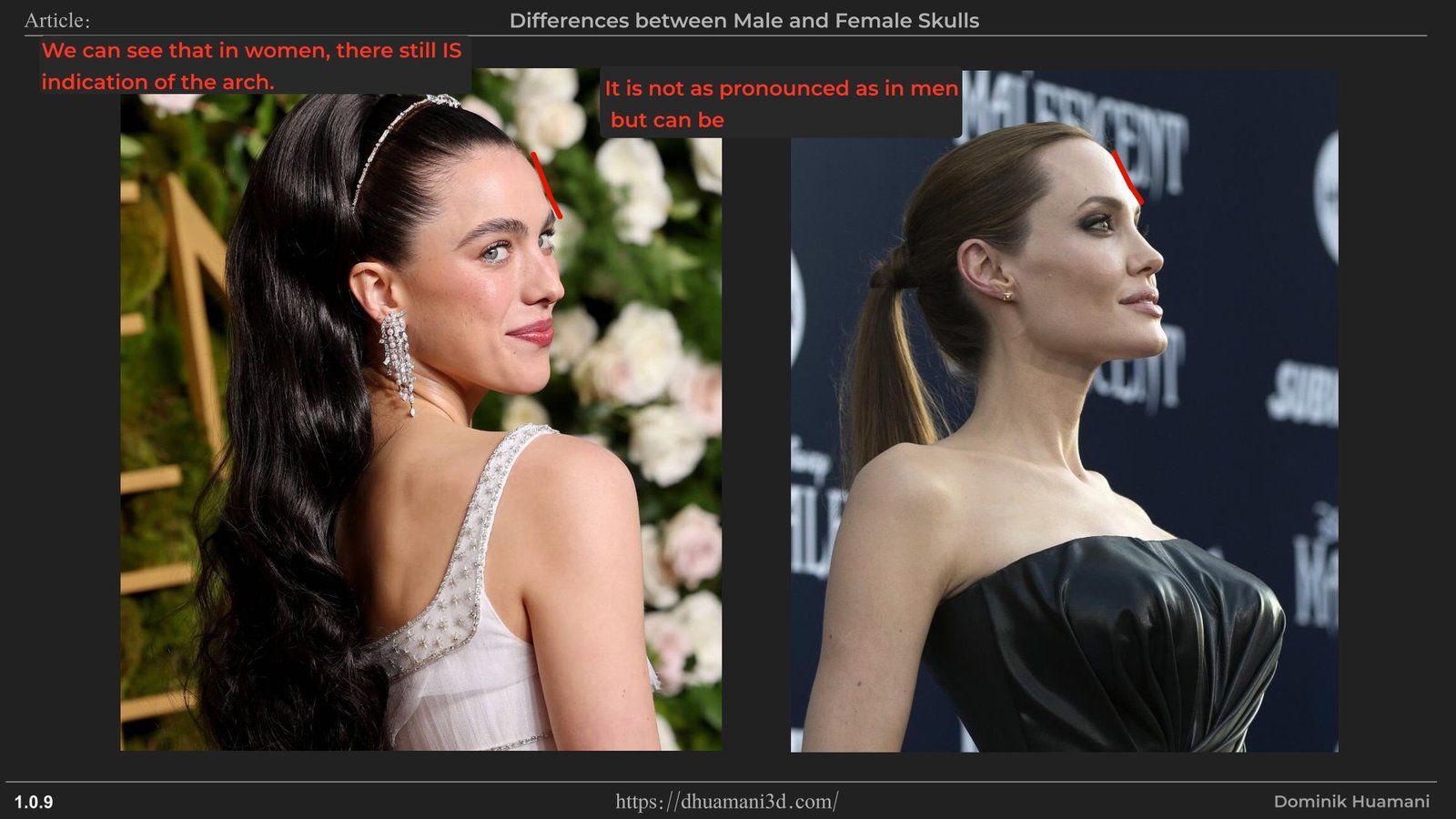
Usually glabella is more visible from a profile. As man have more prominent eyebrows, it leads to glabella having larger angle change which is also sharper compared to women with glabella more curved and smoother.
The Supercilliary Arches are visible bump slightly above a place where eyebrows grow. The bump is often smooth looking but if simpified it would make a roof shape form.This is one of the male dominant feature, which is used to create angry, dominant, if overgrown then even "barbaric" energy.
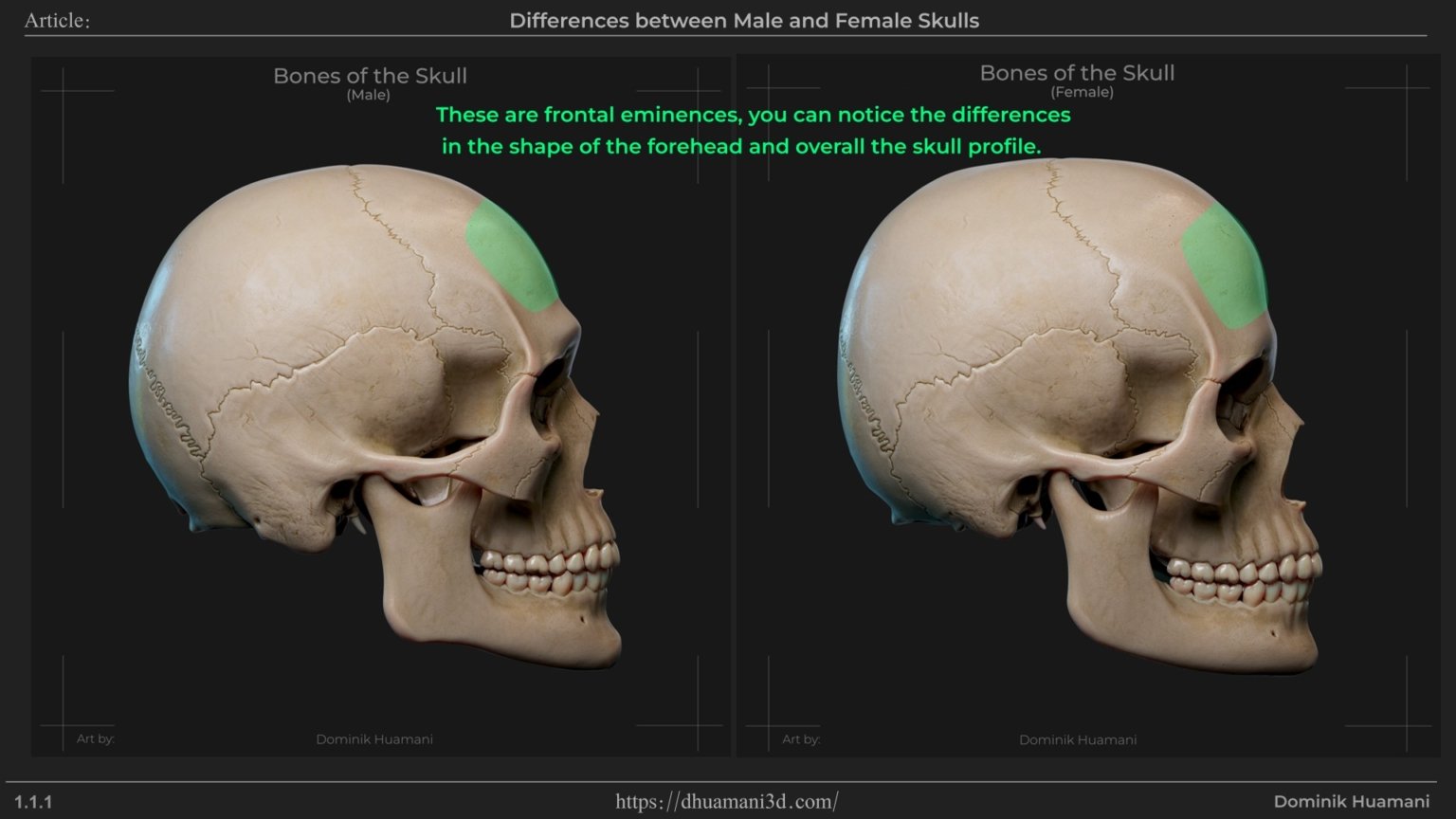
Frontal Eminence
Since we’re already on the topic of the forehead, let’s talk more about it.
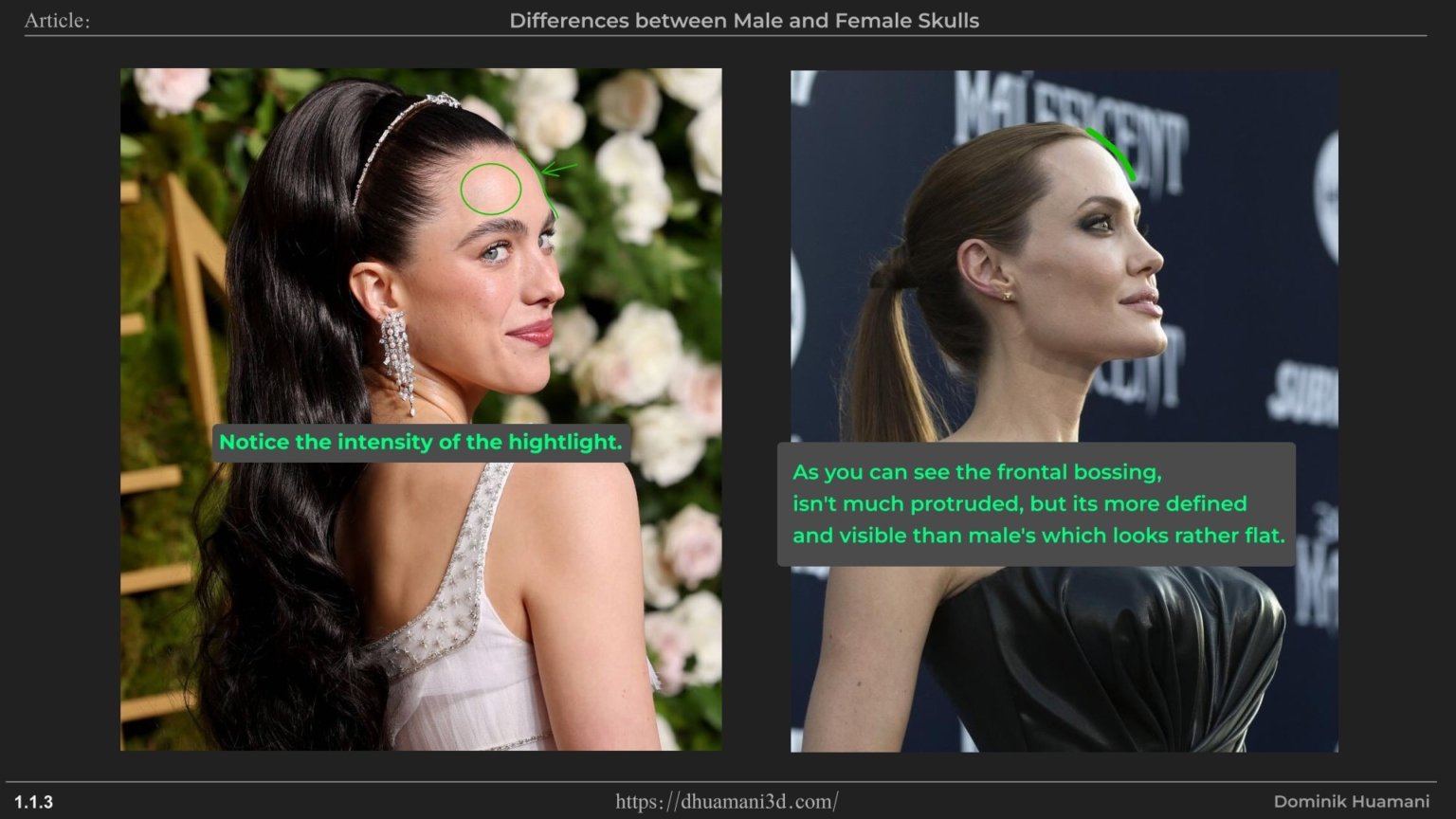
The frontal eminence, also called frontal bossing, basically refers to the forehead and the way it projects forward in certain people. Sometimes it can look like indication of two horns which coincidentally, it’s more common in women than in men.
This is because women typically have a less pronounced superciliary arch (eyebrow area) and a smoother forehead, making the frontal bossing appear more visible.
So, the main difference here would be more prominent frontal bossing in women, and less in men.
Eyes and Cheek Bone
Moving a bit lower, we get to the eyes and cheeks.
Regarding the eyes, I want to mention two things:
1. The Supraorbital Margin:
This is the upper rim of the eye socket, just below the eyebrow arches. In women, it is generally thinner than in men. Visually you won’t notice in real life because it’s covered by soft tissue(fat), but in skulls it’s something worth noting as it would most likely have more damage or noticable Subsurface Scattering in stronlgy lit environments.
2. The Lateral edge of the eye socket:
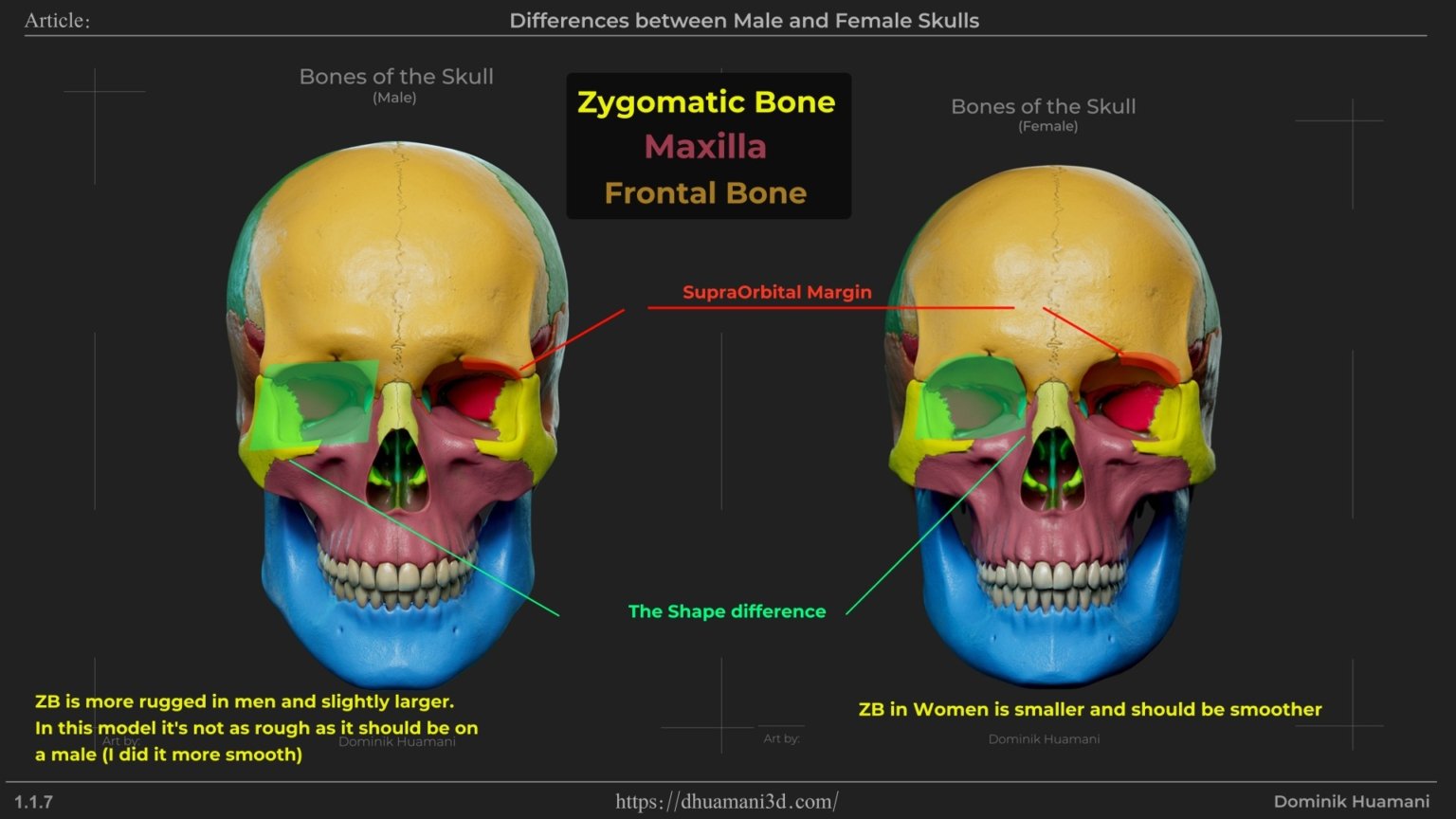
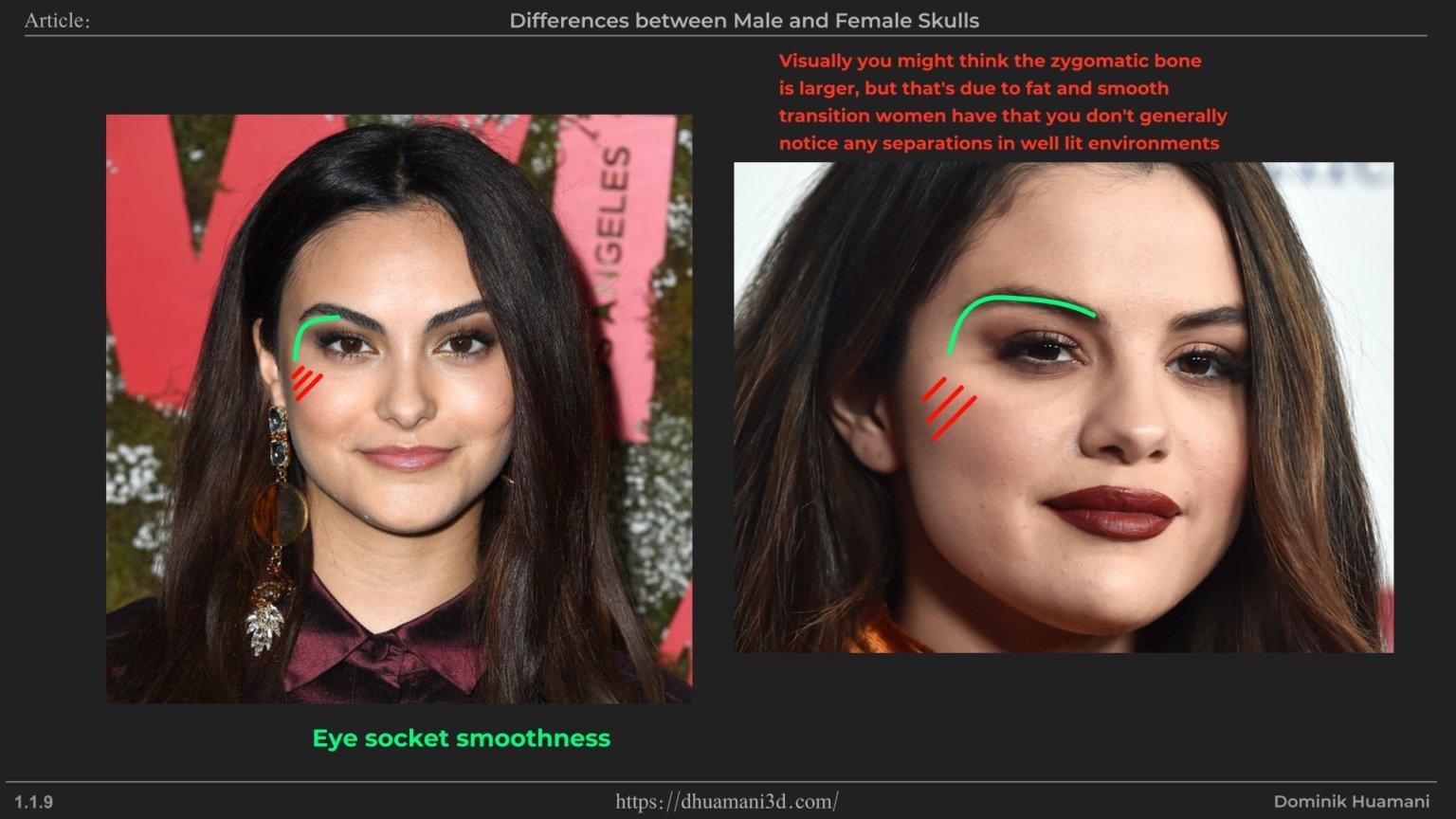
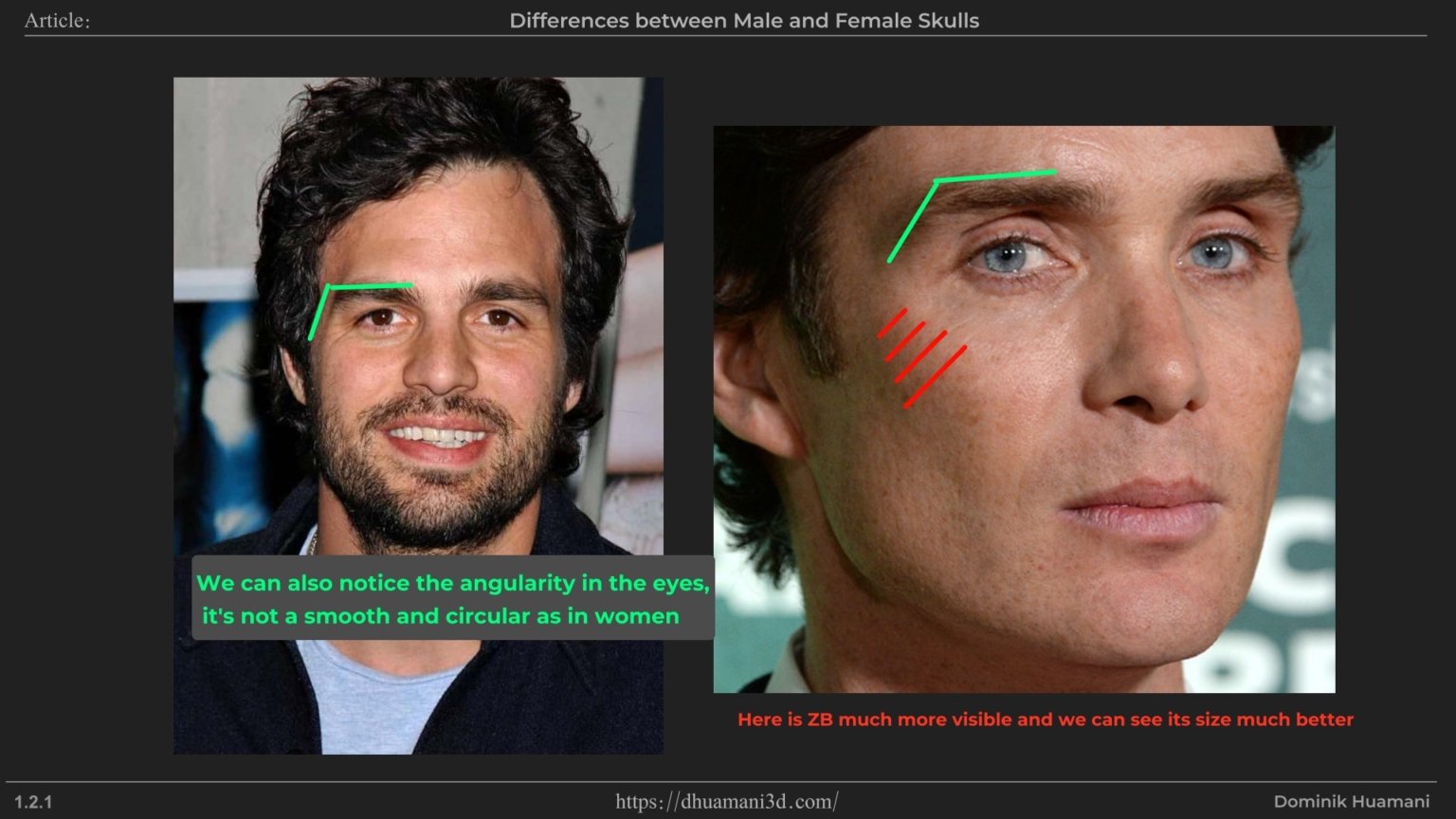
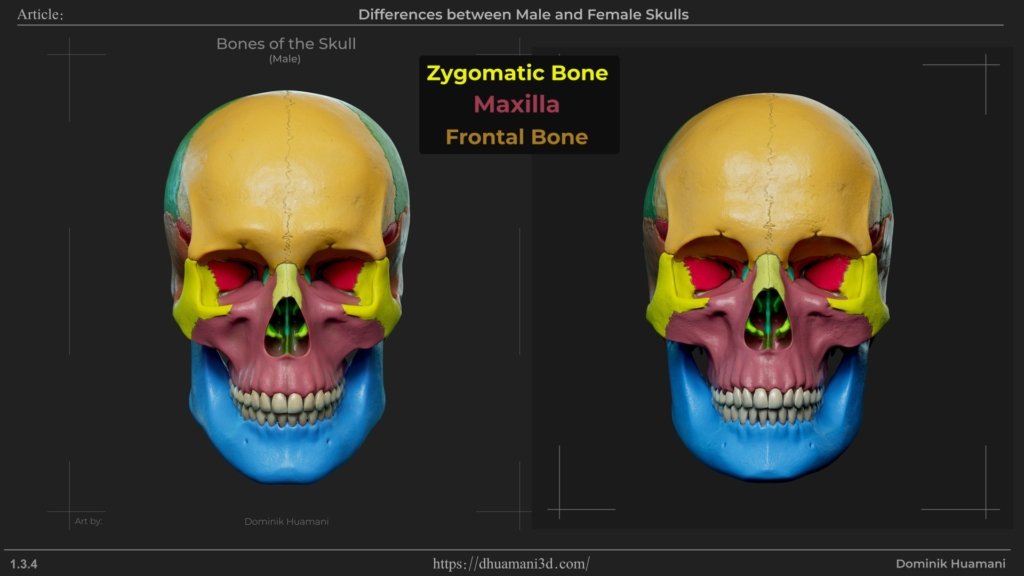
Where the zygomatic bone (cheekbone) meets the frontal bone. In men, this angle is straighter, while in women it’s more rounded. This often makes feminine faces appear smoother or more circular in that area, while in men it tends to create a straighter, more defined line.
Both male and female eye sockets are squarish in shape, but female sockets are generally smoother which leads to more circular shapes.
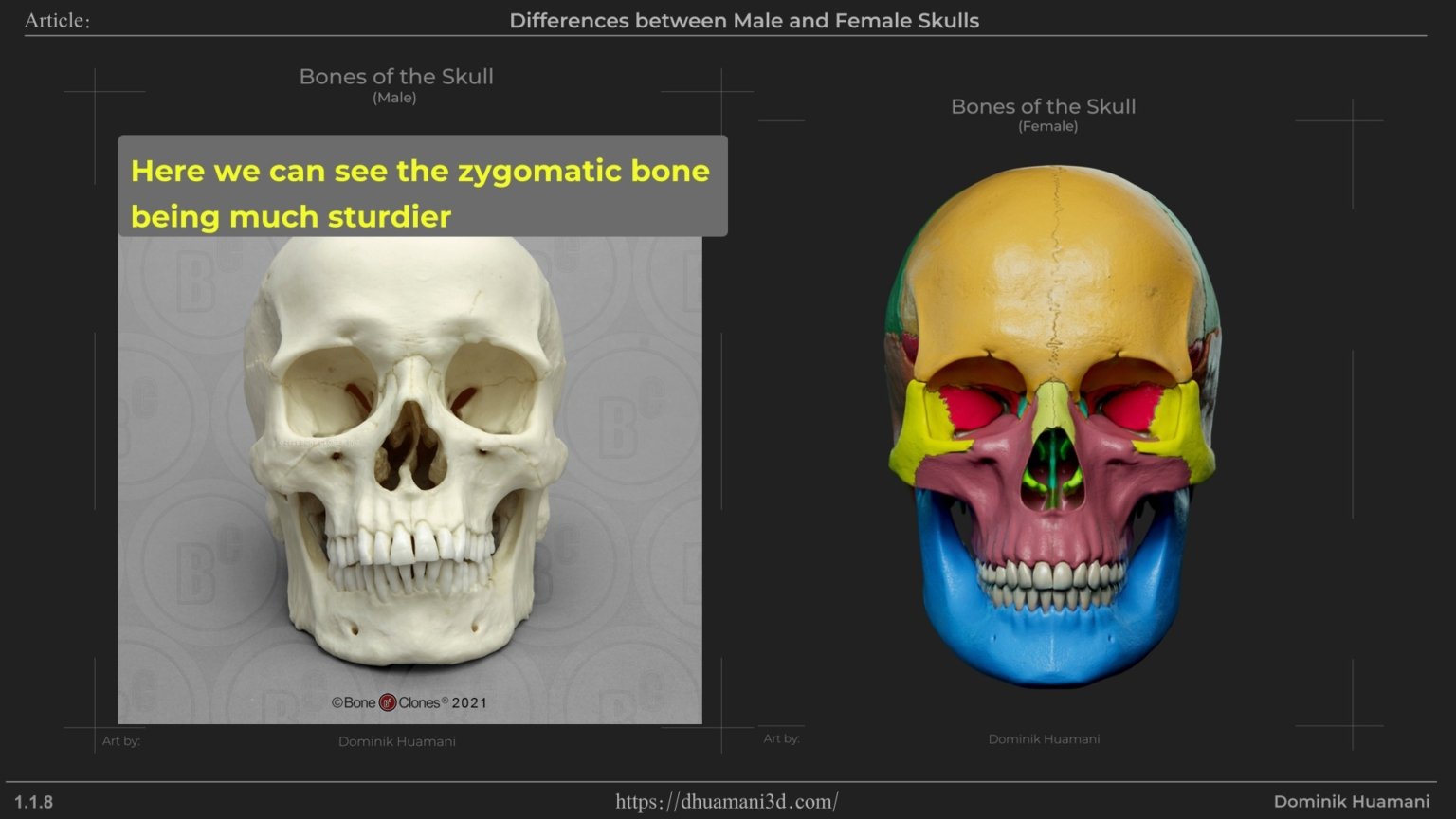
Zygomatic bone (cheekbone) is another feature with strong difference. In men, it’s larger, but in women, cheeks can appear fuller due to soft tissue, especially at younger ages. With aging, the bone structure can become more visible, making the difference clearer as the tissue fades away.
Mandible and Teeth
Mandible width is often associated with masculinity. Generally, a wider jaw reads as more masculine, especially when it approaches or exceeds a 90° angle at the jawline.
However, some women have wider jaws and still look feminine.
That's because the main factor here isn’t just the width, but the angle of the mandible. In men, it’s sharper and in women it’s smoother and more transitional. So, you can maintain a feminine look even with a wider jaw, as long as the angle of the mandible remains soft.
Of course, if you push the width to “Giga Chad” levels, it will read as more masculine no matter what.
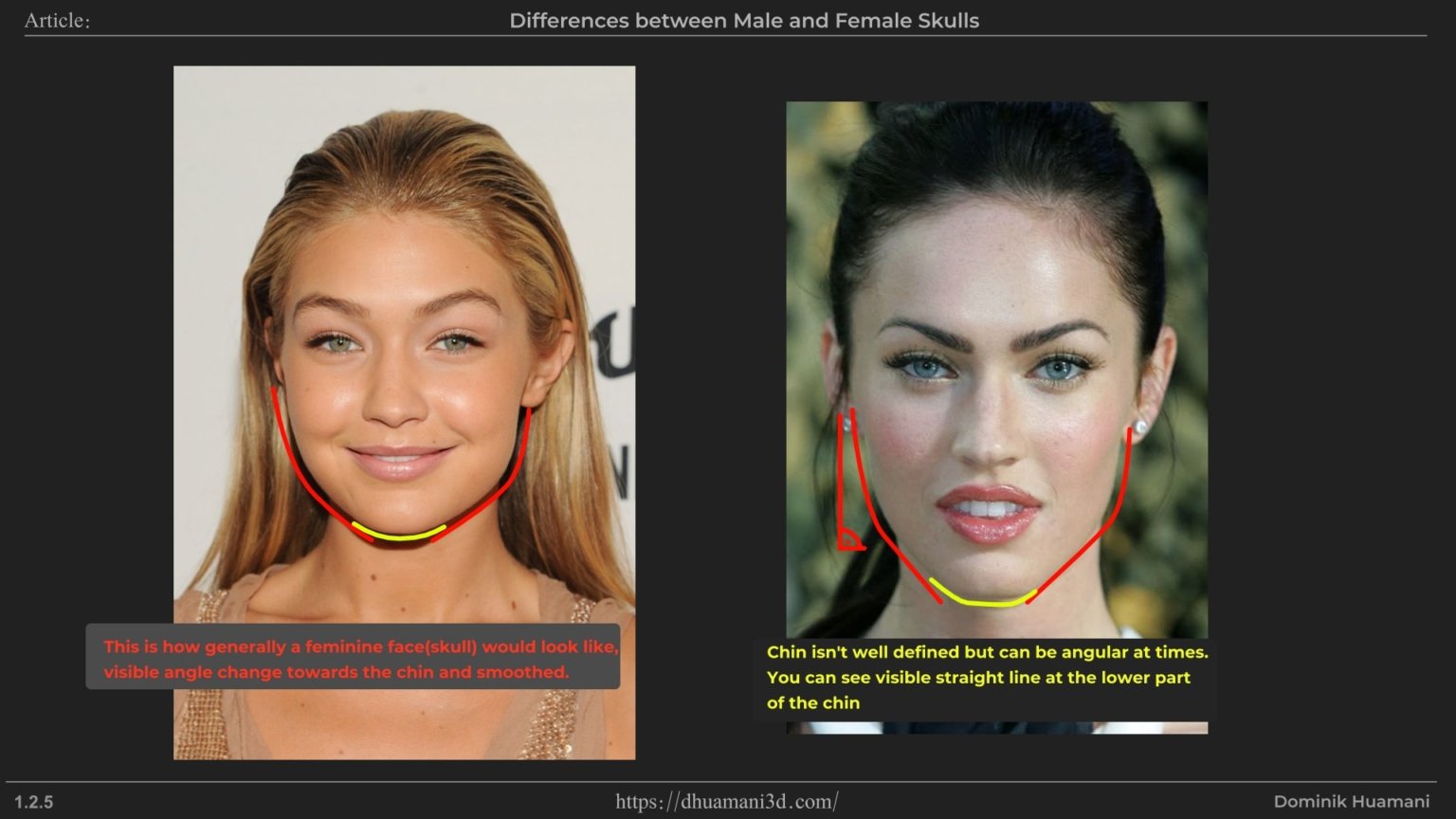
Another important part of the mandible is chin, In Anatomy, this is called the mental protuberance. It’s the triangular shaped bony part at the front of the jaw, with two small bumps (mental tubercles) below it, sometimes producing the so called “butt chin.”
In men, it tends to be more rugged and linear while in women, smaller, smoother, and with fewer hard planar breaks. If you want to keep a feminine look, this is one area to keep soft.
Teeth: Women tend to have smaller teeth because their skulls are generally smaller. This difference isn’t very noticeable in real life unless comparing skulls directly. However, one point of interest is that men often have larger upper canines than women.
Mastoid and Styloid Process
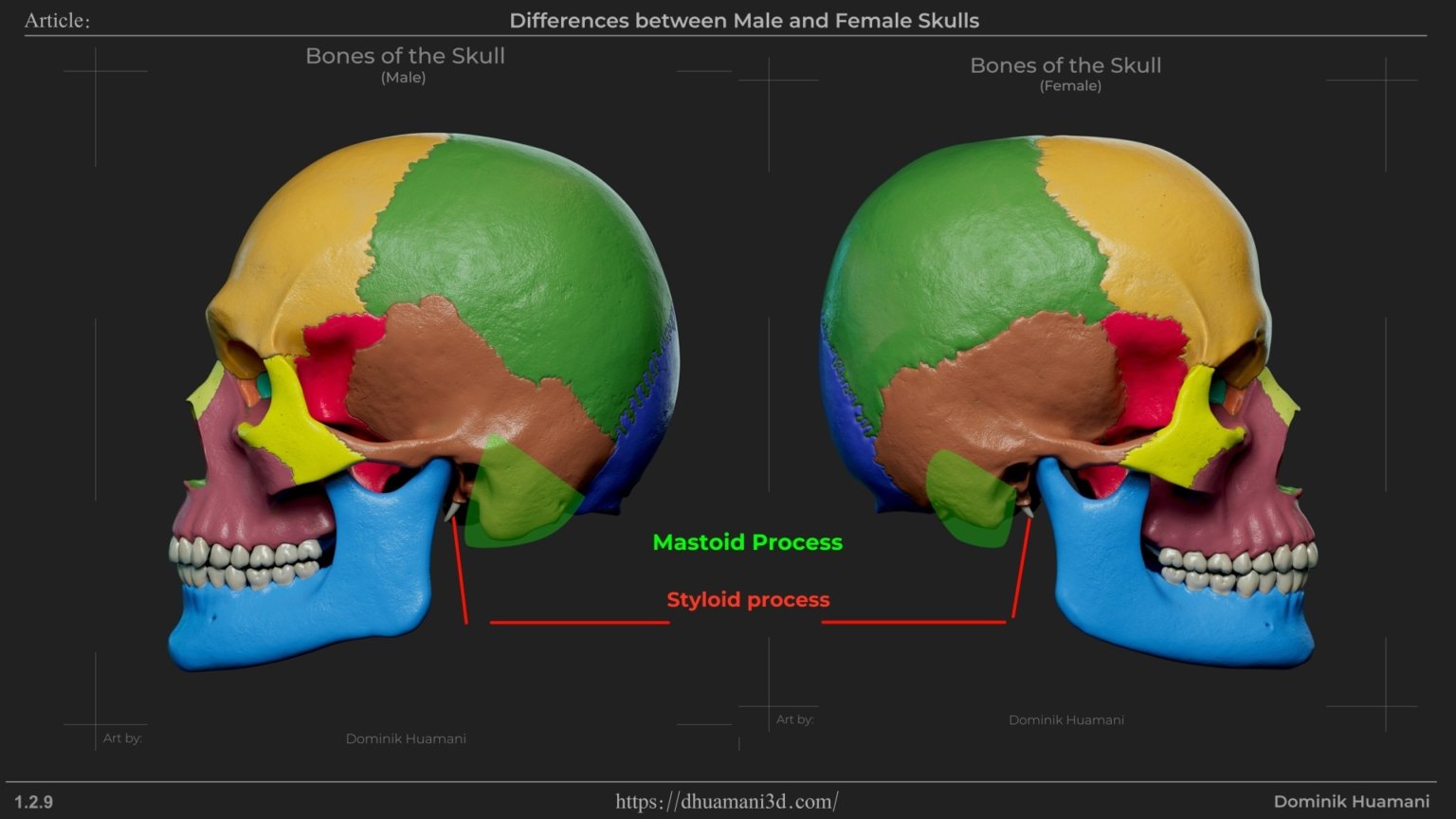
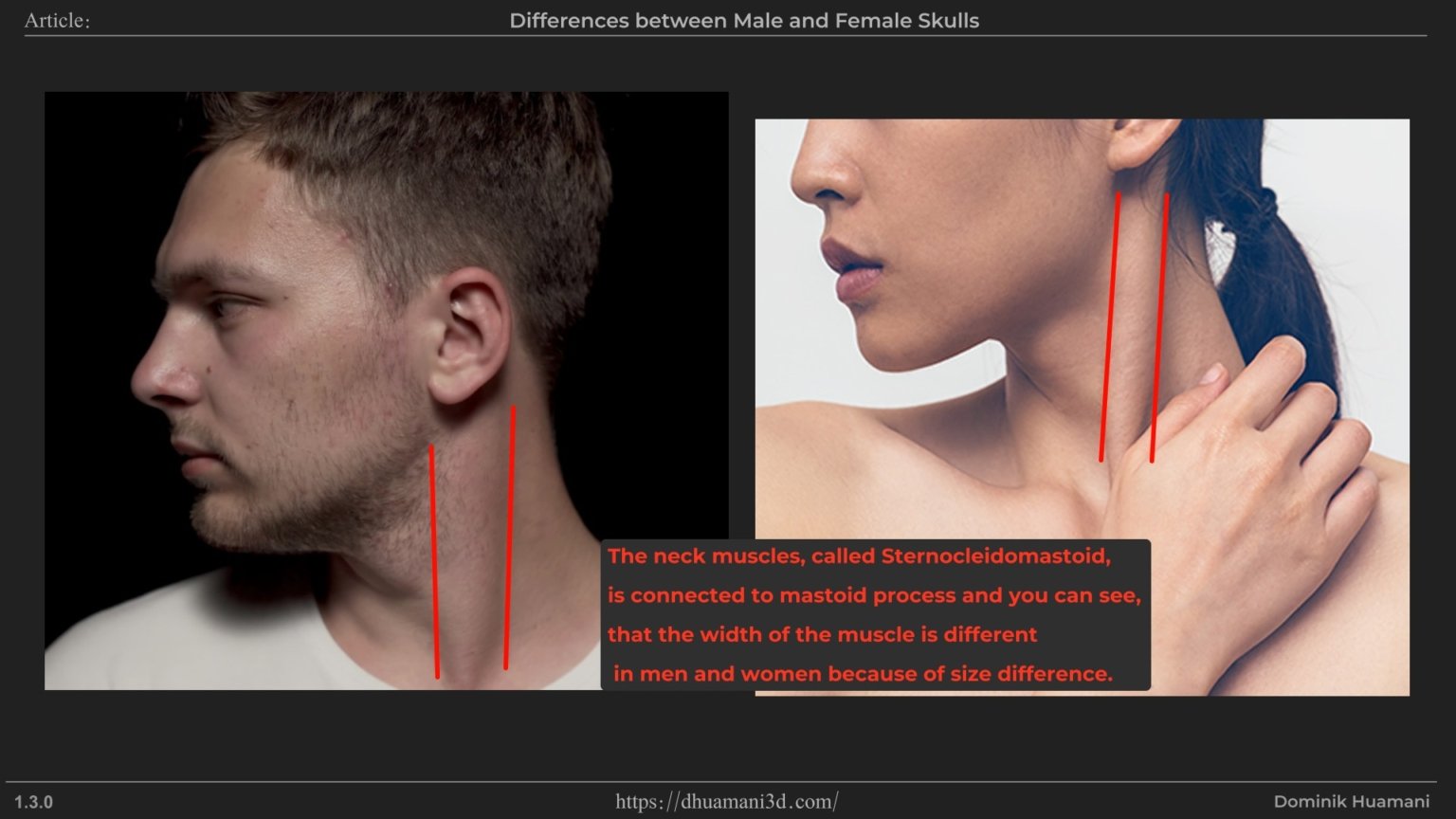
Mastoid Process
This is the bony bump behind the ear where the neck muscle attaches(Sternocleidomastoid). It’s not visible directly in the face, but it affects the width and thickness of the neck muscle. In men, it’s generally larger, contributing to wider looking neck. You can palpate it behind your ear where the muscle ends.
Styloid Process
This small, pointy bone lies deeper, between the mastoid process and the mandible. It serves as an attachment point for several muscles. It’s typically smaller in women. Since it’s deep inside, it doesn’t create a visible difference in the face.
Ethnic Differences in Skulls
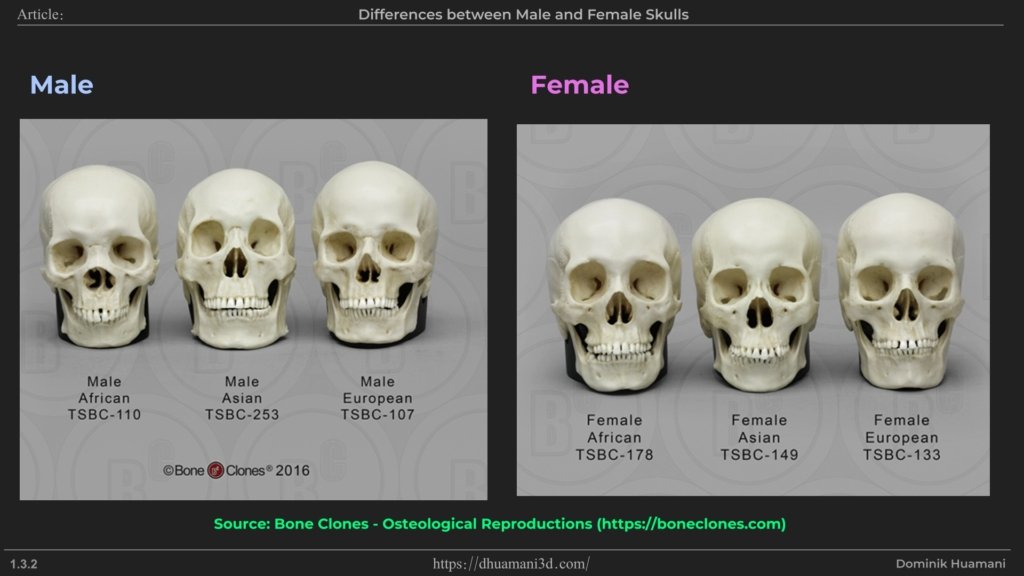
Considering all the differences mentioned above, we have a sort of ‘starting point’ from which we begin our comparisons, and this starting point also varies based on ethnicity. Commonly, skulls are grouped into European, African, and Asian types (with a few other categories less used today).
European
Eye sockets – Rounded corners with an overall squarish shape.
Nasal bridge – Very pronounced, projecting forward with curvature.
Nasal aperture – Narrow, tall, and with a sharper break at the top.
Teeth – Smaller and narrower than other groups.
Skull shape – Often dolichocephalic (longer than wide), with some regional variation.
African
Eye sockets – Very squarish, with a straight upper rim.
Nasal bridge – Wide, flat, and shorter.
Nasal aperture – Very wide and open.
Teeth – Larger gaps between teeth.
Maxilla – More protrusive compared to other skulls.
Skull shape – Often dolichocephalic.
Asian
Eye sockets – More circular and smooth, though not perfect circles.
Nasal bridge – Moderate projection, generally wider than in Europeans.
Nasal aperture – Heart-shaped, wider toward the bottom.
Teeth – More shovel-shaped incisors.
Zygomatic bones – Wider and more forward-projecting.
Skull shape – Often brachycephalic (shorter and broader).
Other Notable Differences
Parietal eminence – (widest point of the skull) – More prominent in women..
Skull Profile – Female skulls are more vertical in profile, male skulls are more sloped and rugged.
Maxilla – Larger in males, which also affects tooth size.
Bone thickness – Overall, female skull cavities are thinner.